
The Budget Deficit
The budget deficit is defined as the excess of the total estimated expenditure over the total estimated revenue. Whenever the government expenditure is more than the government revenue we have the situation of the budgetary deficit.
Let’s look at the formula used to calculate budget deficit:
Total Expenditure = Revenue Expenditure + Capital Expenditure
Total Receipts = Revenue Receipts + Capital Receipts
Budget Deficit = Revenue Expenditure + Capital Expenditure – Revenue Receipts – Capital Receipts
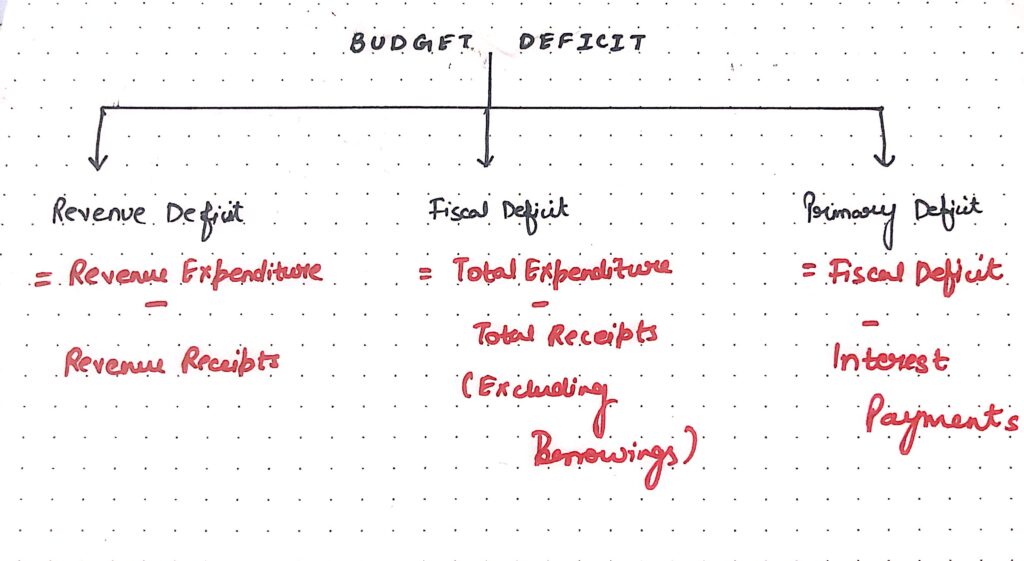
Budgetary deficit has 3 main components:
- Revenue Deficit
- Fiscal Deficit
- Primary Deficit
Let’s understand the concept of the budget deficit in detail.
A quick note: Subscribe to our website to get answers to your curriculum questions.

Revenue Deficit
This deficit occurs in the revenue budget of the government. Revenue deficit refers to the situation when revenue expenditure is more than the revenue receipts during the fiscal year.
Implications of Revenue deficit
The implications or result or the consequences of the revenue deficit are:
- Revenue deficit indicates the inability of the government to meet the expenditure on the routine functioning of the economy.
- It means the dissavings on government account because the government is using the savings to cover the gap between revenue expenditure and revenue receipts.
- It implies that the government has to make up this deficit through capital budget using borrowings and disinvestments.
- The use of capital receipts may lead to an inflationary situation in the economy if the wasteful expenditure by the government is not controlled on time.
- Higher borrowings would increase the future burden to repay the loan amount and interest payments.
Measures to reduce Revenue deficit
Revenue deficit can be reduced by the following ways:
- By reducing public expenditure. For example, removing subsidies, cutting down on non-plan expenditure, etc.
- By increasing revenue. For example, increasing the tax rate, controlling tax evasion, or by increasing the income of the public sector undertakings, etc.

Fiscal Deficit
Fiscal deficit refers to the situation when the total expenditure is more than total receipts excluding borrowing during a fiscal year.
Implications of the Fiscal deficit
Implications or result or the consequences of the fiscal deficit are:
1. Debt trap
Fiscal deficit refers to the total borrowing requirement of the government. Borrowings creates the problem of the repayment of loans and regular interest payments.
Since interest payments are a part of the revenue expenditure, it causes an increase in revenue deficit. The government borrows more money to repay the previous loans, this process keeps on repeating itself and the country falls into the debt trap situation.

2. Foreign dependence
The government also borrows from the rest of the world which causes economic interference by the lending country.
It leads to economic slavery if the lending country imposes its terms on the borrowing country.
3. Causes inflation
The government resorts to borrowings from the Central Bank (Reserve bank of India) to meet the fiscal deficit. This is done by deficit financing (it means printing more currency).
This increases the circulation of money in the economy and creates inflationary pressure if there is an excess supply of money in the economy.
4. Financial burden for the future generation
Borrowing leads to the burden on the future generation through the payment of loans and interest on loans gets accumulated whose burden is to be born by the future generation in the form of more tax and non- tax revenues.

Sources of financing fiscal deficit
1. Borrowings
Fiscal deficit can be met by borrowing from commercial banks, foreign banks, etc.
2. Deficit Financing
The government may borrow from the Central Bank against its securities to meet the fiscal deficit. Central bank issues new currency or prints more currency to meet the fiscal deficit. This process is known as the deficit financing.

Measures to reduce Fiscal Deficit
- Reduce public expenditure. For example, reduce subsidies, or decrease non-planned expenditure.
- Increase in Revenue. For example, an increase in the tax rates and an increase in income of the public sector undertakings.
Primary Deficit
It refers to the difference between fiscal deficit of the current year and interest payment on the previous borrowings.
Implications of the Primary Deficit
- It indicates the amount of the borrowings required to meet the expenditure other than the interest payment.
- If the primary deficit is 0 then the fiscal deficit is equal to the interest payment, which indicates that interest payment on the previous loans had lead to the borrowings.
Measures to reduce Primary Deficit
- It indicates the borrowing requirements of the government to meet the deficit other than the interest payment. Therefore, efforts should be made to reduce the fiscal deficit.
- To reduce the fiscal deficit, the interest payments through repayment of the loan should be done as soon as possible.
Test Yourself
Find Revenue deficit, fiscal deficit, primary deficit, if:
- Capital receipts = 68
- Revenue expenditure = 160
- Interest payment = 20
- Borrowings = 32
- Tax revenue = 50
- Non-tax revenue = 10
Tip: Fiscal deficit should be calculated using the formula; total expenditure minus total receipts, and it always equals the borrowings.

Thank You for reading.
You can read the related post on macroeconomics:
Types of Employment Equilibrium
Concept of Short-Term Equilibrium
Feel free to join our Facebook group and subscribe to this website to get daily educational content in your mailbox.
Happy Learning!
Disclosure: Some of the links on the website are adds, meaning at no additional cost to you, I will earn a commission if you click through or make a purchase. Please support so that I can continue writing great content for you.


