
Resources and Development (Part-2)
We have understood the meaning of resources, interdependence between nature, technology, and humans, and the brief classification of resources. In this blog post, we will understand the details about the Types of Resources. This is a part of the resources and development chapter of class 10 geography, as prescribed by CBSE. Let’s check it.
Feel free to join my Facebook group made for Social Studies and you can also subscribe to my website to receive a monthly mail on all the collated posts. Also, subscribe to my YouTube channel to get video explanations of the topics.
Also, start making notes and revise them over and over again!

Types of Resources
Remember the code as DOEO; where
D- Development status; how much resources are developed or have the caliber (potential), what all resources are available in store (stock) and what all we are keeping saved for the future(reserves)
O- Origin; what is a start of resources, that is some are living(biotic) and some are non-living(abiotic)
E- Exhaustibility; usage of resources; some resources can be reproduced even if we continue to use them over and over again(renewable) and some resources are about to get finished and will take millions of years to reproduce(non-renewable)
O- Ownership; who is the owner of such resources? It could be personal private property (Individual), or for the whole society (community), it can belong to a nation(national) or it could be available for the whole world(international)
Let’s understand and learn in the above sequence only.
1. Development Status; D
On the basis of development status, resources are of 4 types:
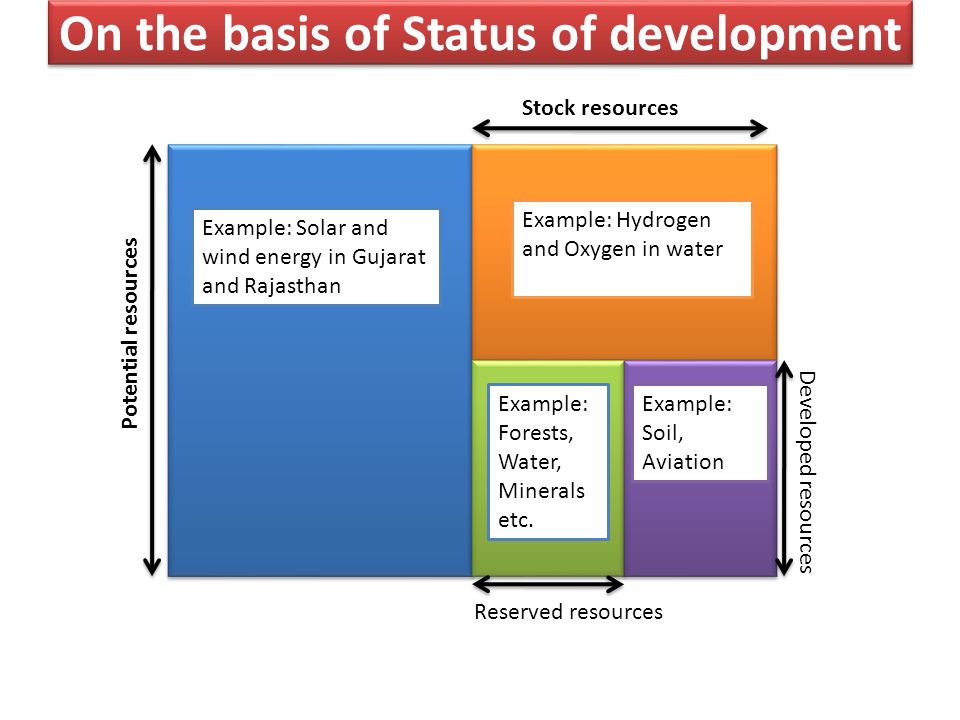
- Potential Resources are those which are not developed properly. For example, solar and wind energy in Gujarat and Rajasthan.
- Developed Resources are those whose quantity and quality have been determined for using them.
- Stock is that material in the environment that can satisfy human wants but humans do have the required technology to use them. For example, hydrogen and oxygen in the water.
- Reserves are a subset of stock, these resources can be used with the help of the available technology, but their use has not started. For example, forests, river water, etc.
2. Origin; O
On the basis of origin that is, from where the resources originate or come from; resources are classified as; biotic and abiotic. Remember it, with a sound of a sheep “BA BA”
- Biotic resources mean which are obtained from the biosphere and are living like us; human beings, flora means plants, fauna means animals, fishes, etc.
- Abiotic resources are non-living things like rocks, metals, stones, etc.
3. Exhaustibility; E
On the basis of exhaustibility, that is, the usage of resources, they are classified as renewable and non-renewable.
- Renewable resources mean which can be renewed or reproduced by the nature with their physical, chemical, and mechanical processes. They are also known as replenishable resources. For example, solar and wind energy, water, forests, wildlife, etc.
- Non-renewable resources can not be renewed easily and it takes millions of years to form. For example, minerals and fossil fuels.
4. Ownership; O
On the basis of ownership, that is, who is the owner of the resources, they are classified as:
- Individual Resources could be the private property of anyone. Many farmers own land, urban people own plots, houses. So, any resources which belong to some particular person are individual resources.
- Community resources are owned by the community or society and anyone can use them, mostly they are used by all the members of a community. Common grazing grounds, burial grounds, public parks, picnic spots.
- National Resources are those which belong to the nation. The country has the legal power to take over any private property for the welfare of society. All the minerals, forests, wildlife, within the political boundaries, and oceanic area up to 12 nautical miles (22.2 km) are a part of national resources.
- International Resources which belongs to international institutions. The oceanic resources beyond 200 nautical miles belong to the open ocean and nobody owns it.

Thank You So much for reading the above content.
This is the second post on Resources and development. I am going to produce more such blog posts.
Feel free to join my Facebook group made for Social Studies and you can also subscribe to my website to receive a monthly mail on all the collated posts. Also, subscribe to my YouTube channel to get video explanations of the topics.
Take a look at the previous blog posts on resources and development.
Disclosure: Some of the links on the website are ads, meaning at no additional cost to you, I will earn a commission if you click through or make a purchase. Please support me so that I can continue writing great content for you.


